Understanding Default Gateway: It’s Not Always the Router

Hi folks, thanks for stopping by.
In this article, I want to explain default gateway, or more specifically, IP default gateway, in a simple and practical way.
As beginners, many of us learn that the IP default gateway is always the router’s IP address. While this is often true, it’s not always the case.
What Is a Default Gateway?
Simply put, a default gateway is the exit path of a network.
When a device wants to send traffic outside its local network and doesn’t know where to send it, the traffic will be forwarded to the default gateway.
Because of this, the IP default gateway is the IP address we assign as the way out of the local network.
The important thing to understand is this:
Default gateway is not about the IP number itself, but about the device behind that IP.
Why Is the Router Usually the Default Gateway?
In most basic network setups, the router becomes the default gateway because a router:
- Has a routing table
- Can forward packets between different networks
- Is designed to connect multiple networks
That’s why, in simple topologies, the router IP is commonly used as the default gateway.
When Is the Default Gateway Not a Router?
In more advanced setups, things can be different.
For example, in a network that uses a Layer 3 switch, inter-VLAN routing can be done directly on the switch. In this case:
- The client’s default gateway can be the Layer 3 switch IP
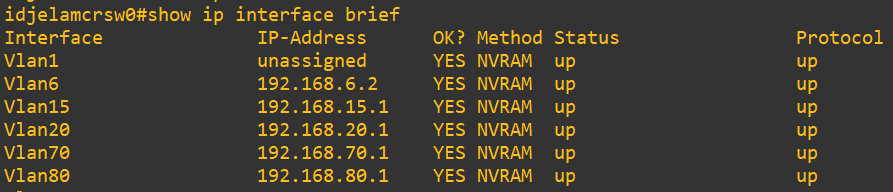
- The Layer 3 switch’s default gateway points to the router
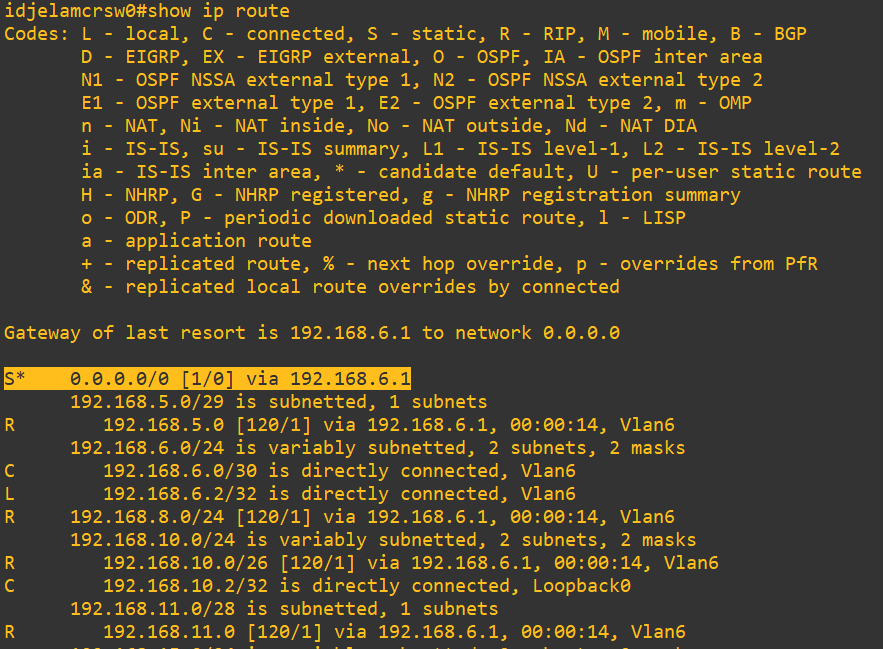
- The router’s default gateway points to the ISP
Here, the default gateway is chosen based on routing capability, not device type.
Devices That Can Act as a Default Gateway
Generally, a device can become a default gateway if it:
- Has a routing table
- Can make routing decisions
Common examples include:
- Routers
- Layer 3 Switches
- Firewalls
Final Thoughts
So, does a default gateway always have to be a router IP?
Not always.
The key takeaway is simple:
Default gateway is about function, not the IP address.
As long as the device behind the IP can perform routing, it can act as a default gateway.
Hope this article helps clarify the concept.
See you in the next post 🚀
